Accessing the Agent API
To access the API details for a specific agent, navigate to your agent’s configuration within Lyzr Studio. You will find an “Agent API” button, which provides the necessary endpoints and instructions for integration. Clicking this button will typically reveal information such as your API key, agent endpoint URL, and example request/response structures.
Clicking this button will typically reveal information such as your API key, agent endpoint URL, and example request/response structures.
API Request Body
When making requests to your Lyzr Agent API, you will typically send a JSON payload in the request body. The exact structure can vary based on the agent’s configuration and its expected inputs. A common structure involves passing aquery or input field. When interacting with a manager agent (an agent designed to orchestrate or utilize other agents), you must also include details about these managed agents within your API call.
Specifying Managed Agents for Manager Agents
Themanaged_agents array within the API body is crucial when you are interacting with a manager agent. This array explicitly lists the sub-agents that the manager agent has access to and can utilize to fulfill the given query. It informs the manager agent about the specific tools (other agents) at its disposal, including their unique identifiers and descriptive information.
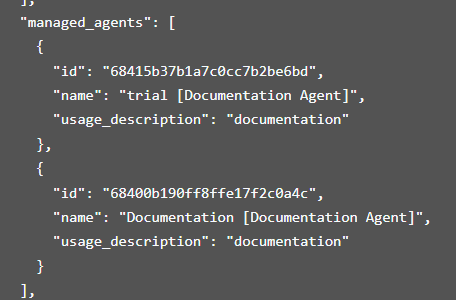
The managed_agents array is a list of JSON objects, where each object represents a sub-agent available to the manager agent, as shown below:
 Each object within the
Each object within the managed_agents array typically contains the following fields:
id(String):- Purpose: This is the unique identifier for the managed sub-agent. It’s an internal ID generated by Lyzr Studio and is essential for the manager agent to correctly reference and invoke the specific sub-agent.
- How to Obtain: You can find this ID in the Lyzr Studio interface when configuring agents or by inspecting API responses that list available agents.
- Example:
"68415b37b1a7c0cc7b2be6bd"
name(String):- Purpose: A human-readable name for the managed sub-agent. This name helps in identifying the agent in logs, debugging, and understanding its role. It often includes a descriptive tag like
[Documentation Agent]. - Example:
"trial [Documentation Agent]"or"Documentation [Documentation Agent]"
- Purpose: A human-readable name for the managed sub-agent. This name helps in identifying the agent in logs, debugging, and understanding its role. It often includes a descriptive tag like
usage_description(String):- Purpose: A brief description of what the managed sub-agent does or what its primary function is. This description helps the manager agent decide which sub-agent is most appropriate for a given task or part of the overall query.
- Example:
"documentation"
managed_agents array in your API request to a manager agent, you enable it to intelligently select and leverage its integrated sub-agents, leading to more robust and capable AI applications that can handle diverse and complex tasks.
